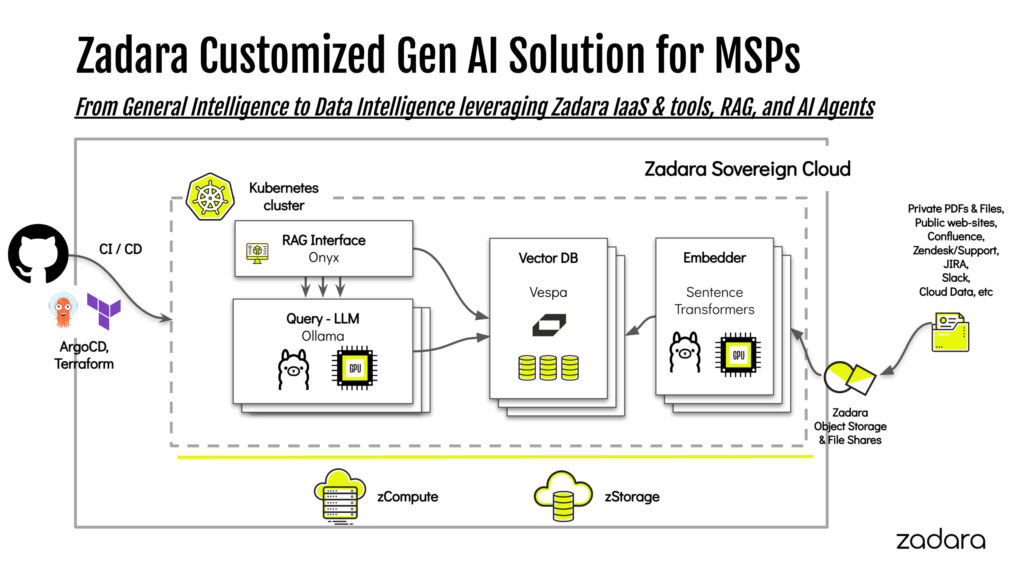
Zadara’s Role in the AI Revolution
At Zadara, we have spent years developing scalable, automated multi-tenancy solutions for on-premises and sovereign edge clouds. Our close collaboration with NVIDIA and partners ranging from enterprises to manage service providers, telecom providers, and NCPs has enabled us to optimize our platform for AI training, AI reasoning, and digital AI sovereignty. We have been adapting our software to fit into the NVIDIA Reference Architecture for NCPs. Moreover, we also developed an entire framework for the deployment of a complete sovereign Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system on an AI factory or NCP. We successfully deployed this system within organizations to provide advanced RAG capabilities for tenants leveraging multiple LLMs supporting digital sovereignty, laying the groundwork for the next wave of AI innovation.

Why Sovereign AI?
In an era where AI is at the core of business innovation, more and more organizations are looking for ways to integrate it into work processes – while maintaining complete data privacy and meeting strict regulatory requirements. This is exactly where Zadara comes into the picture, offering a unique Sovereign AI approach: an integrated edge solution that allows you to implement, manage and operate GenAI systems in a cloud environment and on-prem, without compromising control and security.
Sovereign AI by Zadara Edge Cloud

Key Benefits of a Sovereign AI
Security and Compliance
Our local partners provide strong security features, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring, and ensure compliance with relevant localized data protection regulations.
Sovereign by Design
Each of Zadara’s local Edge Cloud providers ensure data sovereignty by hosting data within the jurisdiction or territory of the government or public entity that owns and operates the cloud service.
Customization and Flexibility
Zadara’s partners each offer customized solutions to meet the specific needs of your organization and offer flexibility in terms of deployment models.
AI Training
Zadara Sovereign AI Edge Cloud brings you the power of artificial intelligence training with efficiency and affordability. Our solutions enable businesses and researchers the full potential of sovereign AI, in any location.
AI Inference
By performing AI Inference on Zadara’s Sovereign AI Edge Cloud infrastructure located close to users, users experience significantly shorter latency, delivering AI inference in near real-time. This is crucial for applications requiring instantaneous decision-making.
Customers using Zadara for AI
Learn how CodeZero leveraged Zadara Sovereign AI Edge Cloud to benchmark ML Training workloads against AWS. Two types of machine images were deployed, one with Nvidia A2 and the other with Nvidia A40. Case scenarios include:

Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Scanning medical images of eyes to detect which patients may be at risk of going blind.
Bert’s A Stock Market Guru
Using a number of industry approved modeling techniques for predicting stock market trends, we then switch to an LLM and deep learning techniques to achieve a higher level of accuracy.
Brain Tumor Radio Genomic Classification
Predict the status of genetic biomarkers important for Brain cancer treatment.
Sovereign AI Use Cases
Sovereign cloud services can benefit a variety of organizations, but they are especially relevant for those that handle sensitive data, such as:
Government Agencies
Governments that require sovereign cloud services for highly sensitive data, including national security information, confidential citizen data, and confidential diplomatic communications, rely on Zadara for complete control over the location of their data.
Public Institutions
Public institutions, such as healthcare providers, educational institutions, and public utilities, often store and process large amounts of personal data. Sovereign cloud services provided through Zadaras partners can help ensure this data is secure and protected.
Financial Institutions
Banks and other financial institutions handle highly sensitive data such as financial transactions, customer account information, and trade secrets. A sovereign cloud service from Zadara can provide the necessary security and privacy required for such data.
Defense and Military Organizations
Military organizations deal with highly confidential data related to national defense, intelligence, and security. A Zadara sovereign cloud provider can deliver the necessary security and protection for such data.
Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs often lack the resources to invest in their own IT infrastructure and security measures. A Zadara sovereign cloud can provide an affordable and secure cloud computing solution that meets their needs.
Zadara and its partners help organizations that handle sensitive data benefit from sovereign cloud services to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
Find out how to easily Implement Ollama (Private LLM) and OpenWebUI on zCompute.
A True Sovereign AI Cloud
Some of the largest cloud providers in the world deliver outstanding services, but even though they may deploy equipment in different geographical locations, they all too often operate under legislation of their head quartered organization.
Hyperscale cloud organizations can, and often do, operate under different legislation than sovereign cloud providers. When choosing a cloud provider you want to ensure you have control over your data including:

Ownership and Control
Jurisdiction and Compliance


Customization and Flexibility
Data Sovereignty FAQ
Data sovereignty is a legal principle that determines jurisdiction over data. It specifies that any data collected or stored within a country’s borders is governed by that country’s laws and regulations.
Ensuring data sovereignty involves several key steps:
Understand Legal Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the data protection and privacy laws of the country where the data is stored and processed.
Data Localization: Store and process data within the country to comply with local laws. This might involve using local data centers and cloud service providers.
Contracts and Agreements: Include data sovereignty clauses in contracts with cloud providers and third-party service providers, ensuring they comply with local laws.
Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel within the country can access the data.
Encryption: Use strong encryption methods to protect data both at rest and in transit, ensuring that only authorized entities within the jurisdiction can decrypt the data.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure compliance with local data sovereignty laws and regulations.
Data Governance Policies: Develop and enforce robust data governance policies that align with the legal requirements of the jurisdiction.
Training and Awareness: Educate employees and stakeholders about data sovereignty requirements and best practices to ensure compliance throughout the organization.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively ensure data sovereignty and comply with the relevant legal frameworks.
An example of data sovereignty can be seen in the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR mandates that personal data of EU citizens must be protected according to EU laws, regardless of where the data is stored or processed. Here’s how it works:
Data Localization: A company operating within the EU must store and process personal data of EU citizens on servers located within the EU or in countries that the EU has determined to have adequate data protection laws.
Compliance Requirements: Companies, even those based outside the EU, must comply with GDPR if they handle personal data of EU citizens. This includes implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect the data.
Cross-Border Data Transfers: If data needs to be transferred outside the EU, the receiving country must have equivalent data protection laws, or the company must use specific mechanisms such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) to ensure the data is protected.
Data Subject Rights: Under GDPR, EU citizens have specific rights regarding their personal data, such as the right to access, rectify, and delete their data. Companies must respect these rights and ensure they are upheld.
This example demonstrates how data sovereignty ensures that the personal data of EU citizens remains protected by EU laws, regardless of where the data is physically stored or processed.
Data sovereignty is the principle that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it is collected, stored, and processed. It emphasizes that a nation has the authority to govern the data within its borders and enforce its data protection and privacy laws. This concept ensures that organizations managing data comply with the legal requirements of the jurisdiction where the data resides, protecting the data from unauthorized access and ensuring it is handled according to local regulations.
A sovereign cloud is a cloud computing environment that stores an organization’s data, including metadata, on servers located within the same country. This ensures that the data complies with local laws and is protected from foreign access.
What is sovereign AI? Sovereign AI involves a government or organization maintaining control over AI technologies and the data associated with them.
